These functions construct various sorts of brackets. They construct a matrix
that can be supplied as the bracket argument in primitive_bracket().
Usage
bracket_line()
bracket_square()
bracket_chevron()
bracket_round(angle = 180, n = 100)
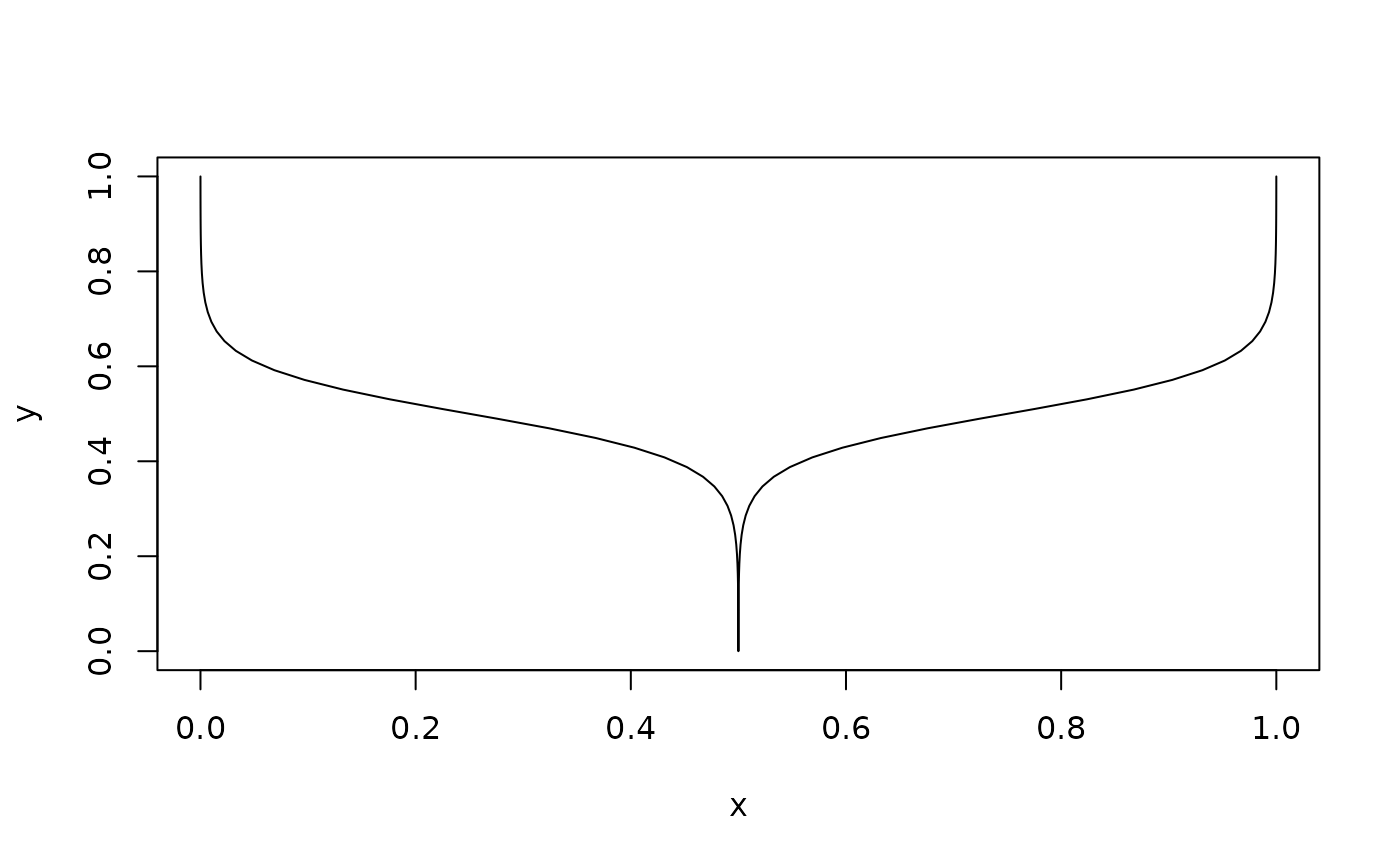
bracket_sigmoid(curvature = 10, n = 100)
bracket_atan(curvature = 5, n = 100)
bracket_curvy(angle = 225, n = 100)Arguments
- angle
A
numeric(1): the angle in degrees for which a circle piece is drawn. Forbracket_curvy(), an angle between 180 and 270.- n
An
integer(1)number of points to use for the bracket.- curvature
A
numeric(1)that controls the curliness of the bracket. More precisely, it is used to construct the sequenceseq(-curvature, curvature, length.out = n)over which the logistic or arctangent functions is evaluated.
Details
When designing custom bracket shapes, the expectation is both columns are are a number between 0 and 1. The first column follows the direction of the guide whereas the second column is orthogonal to that direction.
Functions
bracket_line(): A simple line as bracket. Hasn = 2points.bracket_square(): A square bracket. Hasn = 4points.bracket_chevron(): A chevron (V-shape) that makes a bracket. Hasn = 3points.bracket_round(): One circular arc that makes a bracket.bracket_sigmoid(): Two sigmoid curves stacked on top of one another to form a bracket.bracket_atan(): Two arctangent curves stacked on top of one another to form a bracket.bracket_curvy(): Four circular arcs that make a bracket.
Examples
plot(bracket_sigmoid(), type = 'l')