Colour space scales
scale_chromatic.RdThese scales map the values of colour_spec vectors to coordinates in a
colour space.
scale_colour_rgb(..., aesthetics = "colour") scale_fill_rgb(..., aesthetics = "fill") scale_colour_hsv(..., aesthetics = "colour") scale_fill_hsv(..., aesthetics = "fill") scale_colour_hsl(..., aesthetics = "colour") scale_fill_hsl(..., aesthetics = "fill") scale_colour_hcl(..., aesthetics = "colour") scale_fill_hcl(..., aesthetics = "fill") scale_colour_cmyk(..., aesthetics = "colour") scale_fill_cmyk(..., aesthetics = "fill") scale_colour_cmy(..., aesthetics = "colour") scale_fill_cmy(..., aesthetics = "fill")
Arguments
| ... | Arguments passed on to
|
|---|---|
| aesthetics | The names of the aesthetics that this scale works with. |
Value
A ScaleChromatic ggproto object that can be added to a plot.
Note
Specifying limits, breaks and labels works slightly differently
compared to ggplot2, as these are needed for every channel in a colour
space. When providing these arguments as a vector, a colour_spec vector
describing the arguments for all channels is expected. If provided a
function, the function is applied to every channel. To make it easier to set
these arguments for channels individually, the preferred way is to provide
these arguments with a named list, wherein the names are the first letters
of the channels. For example, you can set the following in
scale_colour_hsv():
To give the hue percent labels, use the default labels for saturation by omission, and set the literal labels for value.
Functions
scale_*_rgb(): Red, Green and Blue colour space.scale_*_hsv(): Hue, Saturation and Value colour space.scale_*_hsl(): Hue, Saturation and Lightness colour space.scale_*_hcl(): Hue, Chroma and Luminance colour space.scale_*_cmyk(): Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Key (black) colour space.scale_*_cmy(): Cyan, Magenta and Yellow colour space.
See also
The colour_spec page for creating colour_spec vectors.
Examples
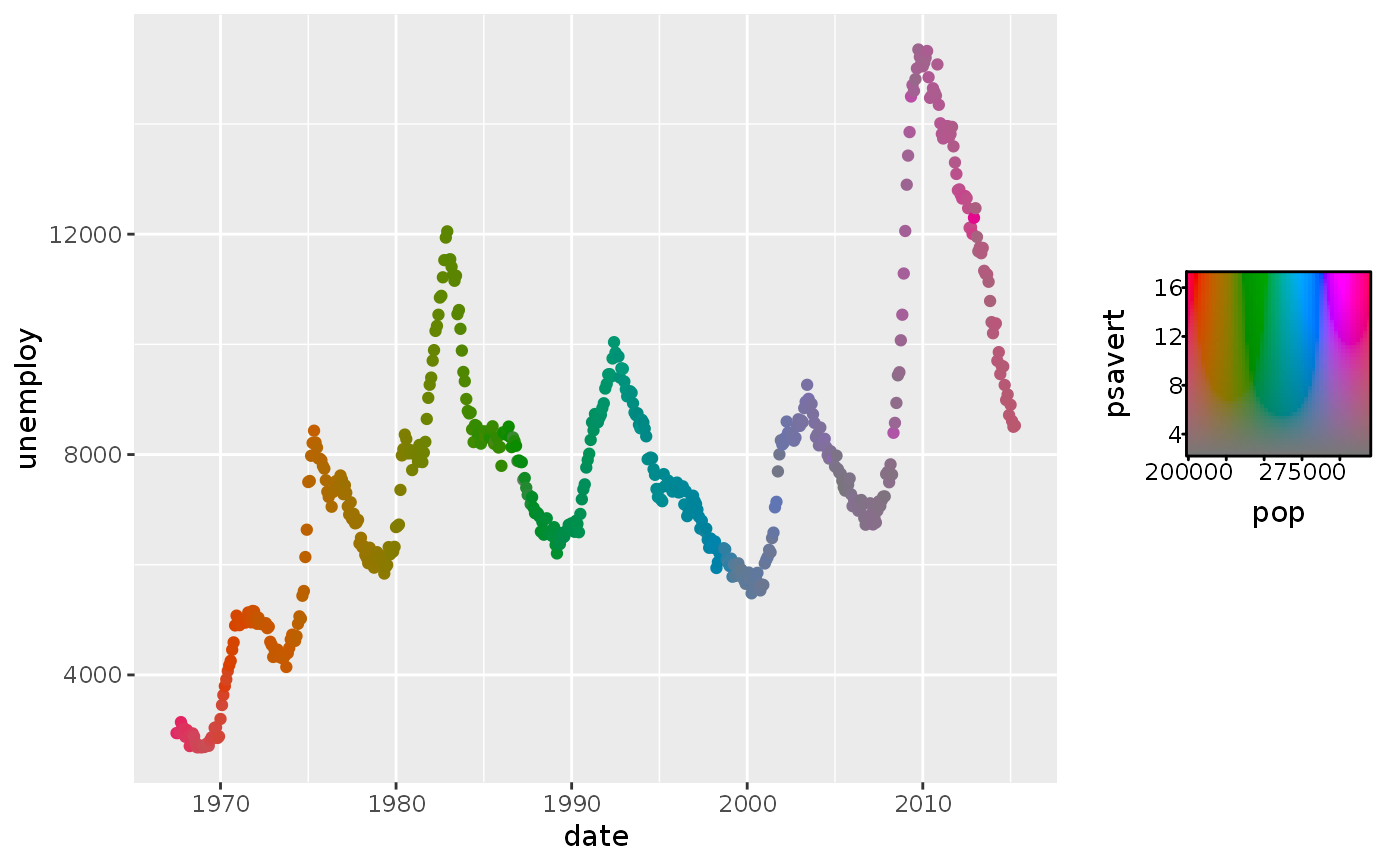
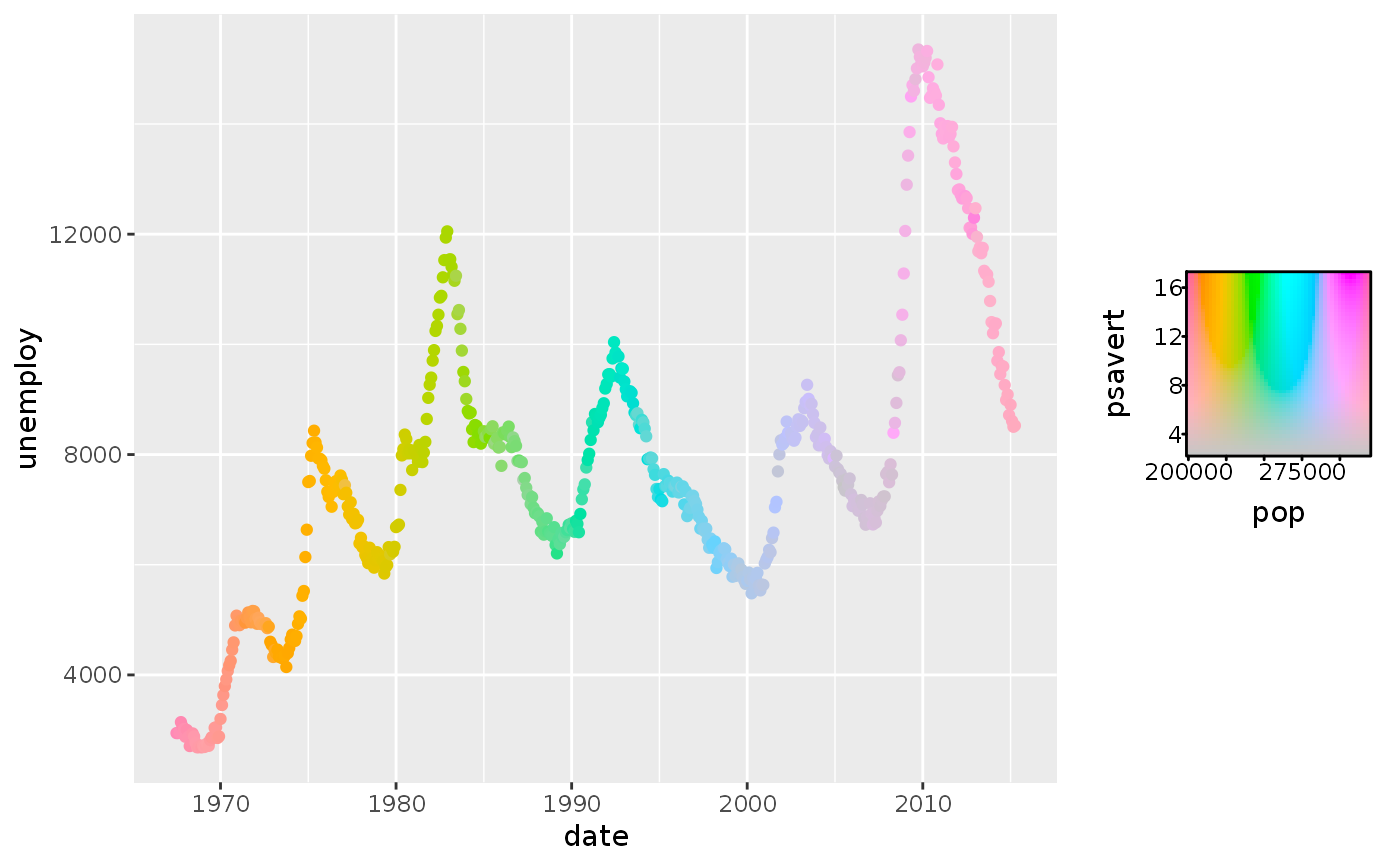
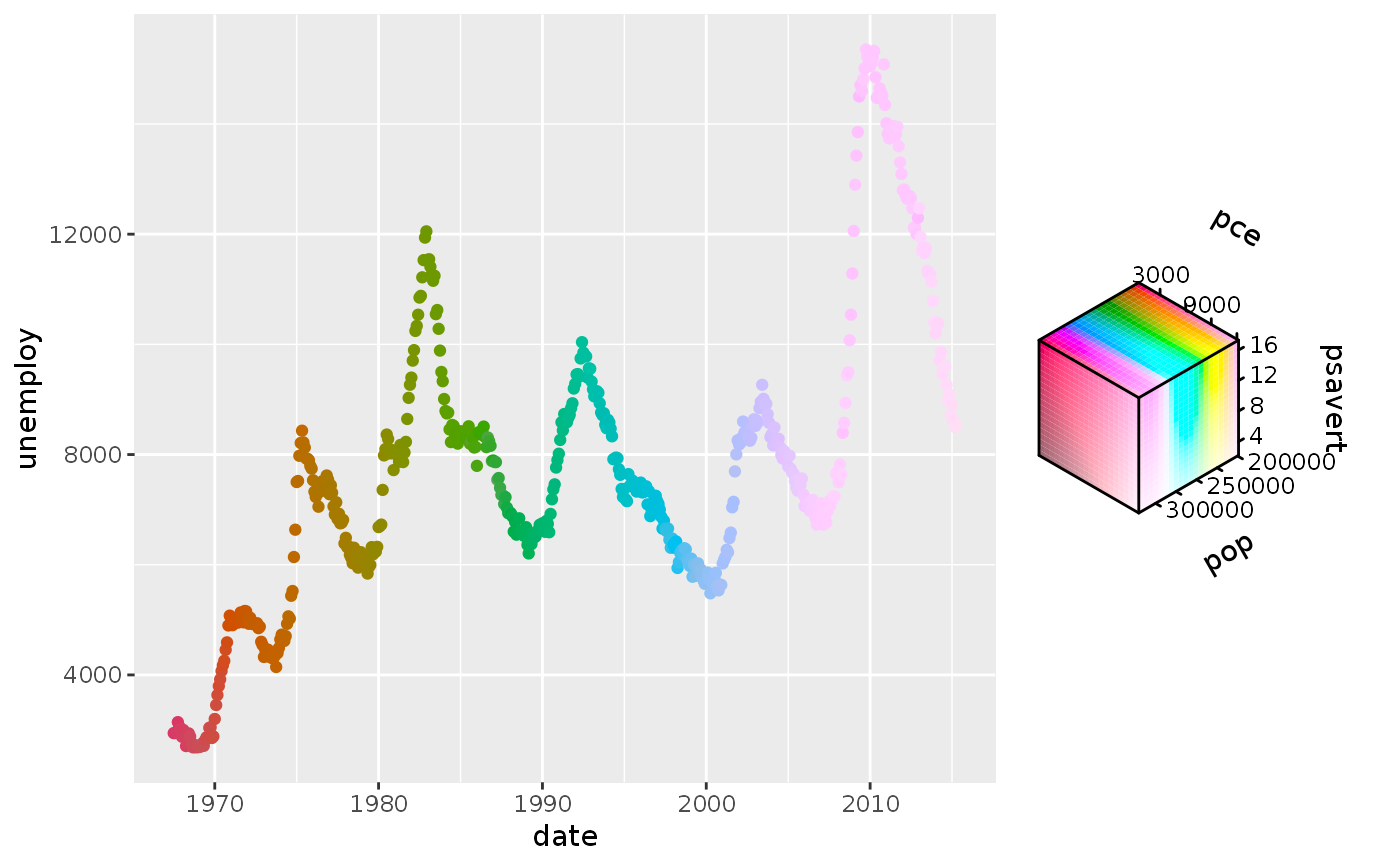
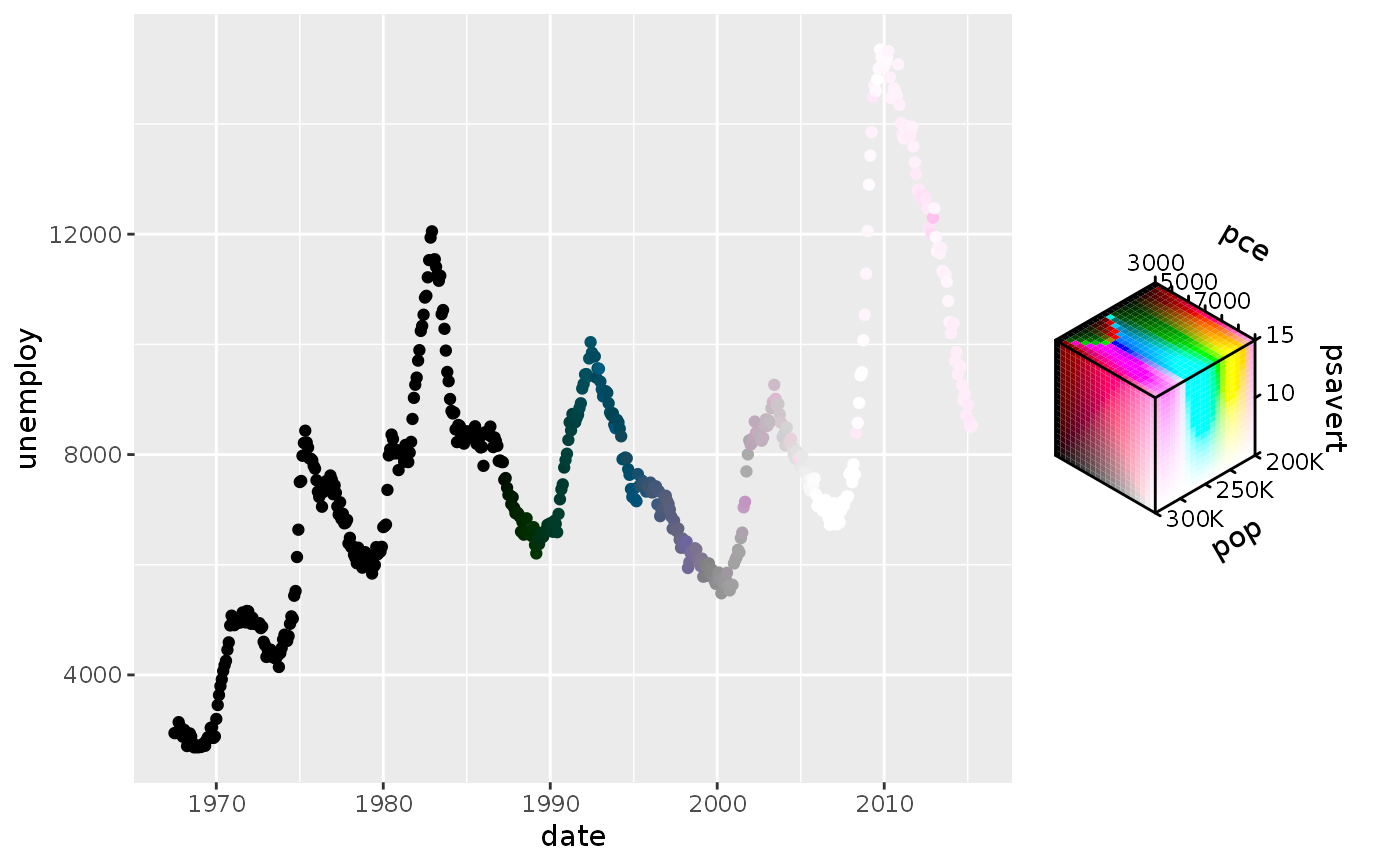
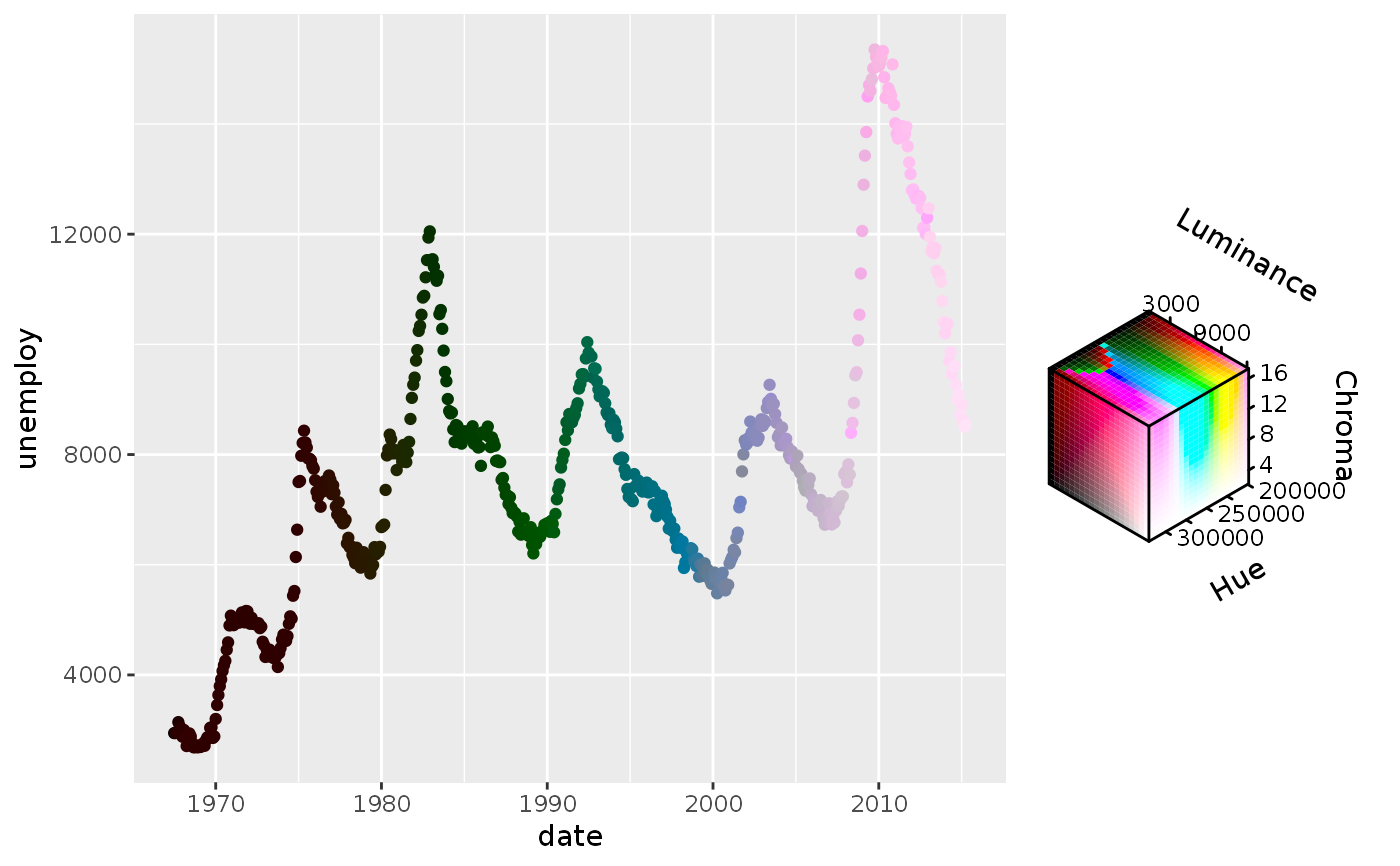
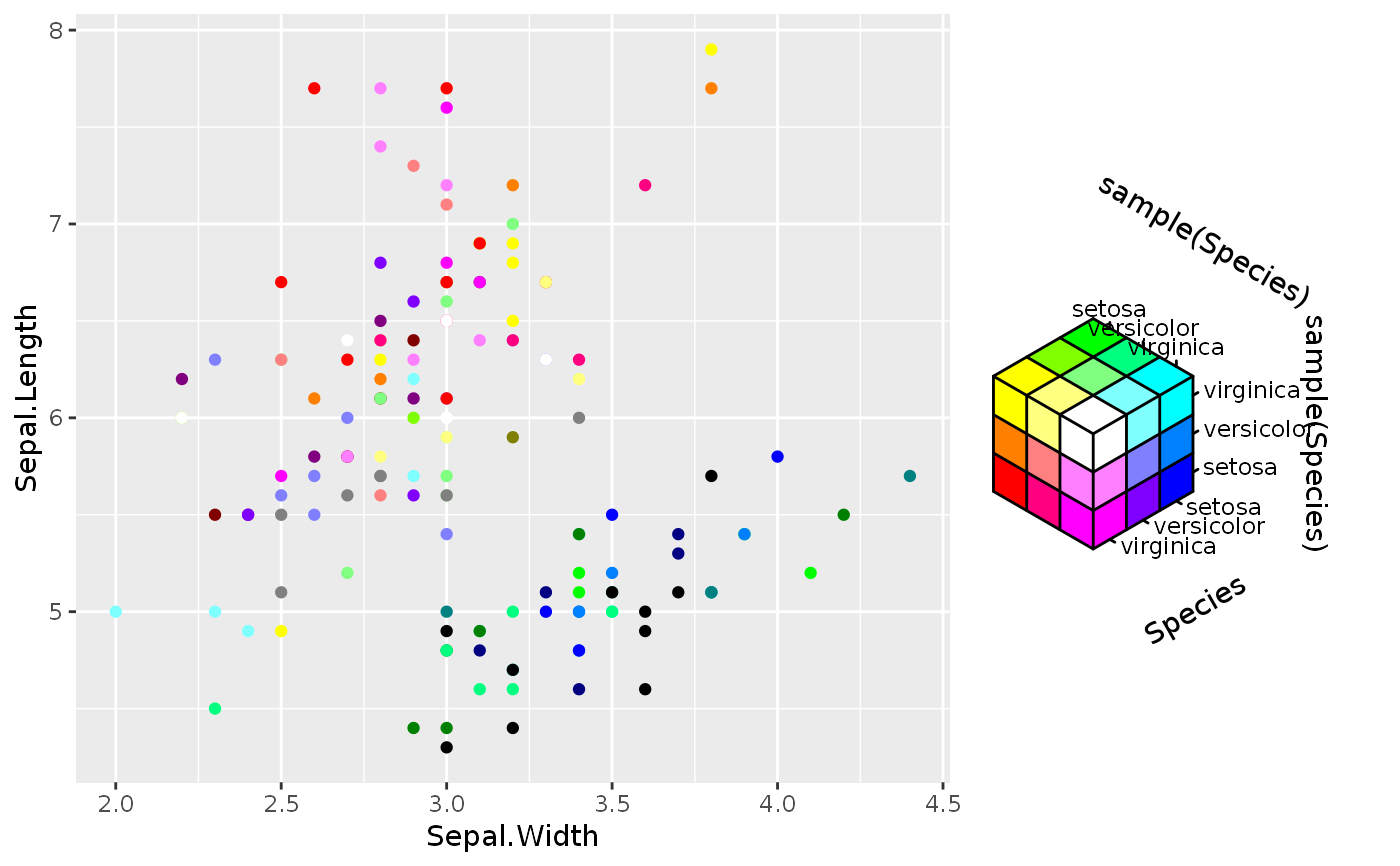
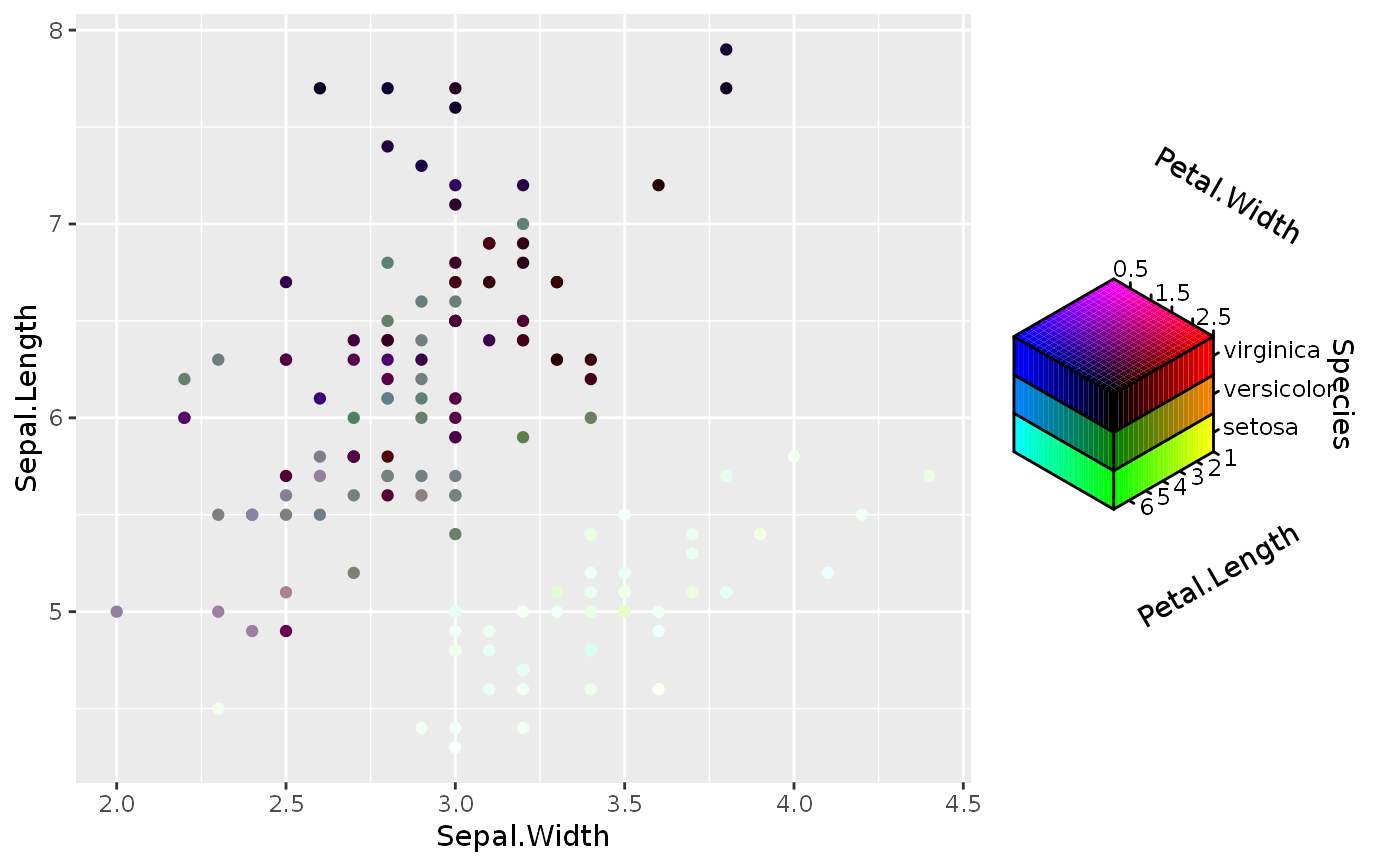
# Empty channels will take the midpoint of the channel limits. # Note that the 'luminance' channel is missing below. p <- ggplot(economics, aes(date, unemploy)) + geom_point(aes(colour = hcl_spec(pop, psavert))) p# You can set the output of missing channels through the channel limits. # Setting 1 value fixes the output for that channel. p + scale_colour_hcl(channel_limits = list(l = 0.8))# Alternatively, you can constrain the output of particular channels. # Setting 2 values between 0-1 restricts the channel output range. p <- ggplot(economics, aes(date, unemploy)) + geom_point(aes(colour = hcl_spec(pop, psavert, pce))) p + scale_colour_hcl(channel_limits = list(l = c(0.5, 1), c = c(0.2, 0.8)))# Setting breaks, labels and limits through named lists p + scale_colour_hcl( breaks = list(c = c(5, 10, 15)), labels = list(h = scales::number_format(scale = 1e-3, suffix = "K")), limits = list(h = c(200e3, 300e3), c = c(5, 15), l = c(3000, 9000)), oob = scales::oob_squish )# Scale can have names for every channel to be displayed in the guide p + scale_colour_hcl(name = c("Hue", "Chroma", "Luminance"))# Scale can handle all-discrete variables p <- ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Width, Sepal.Length)) p + geom_point(aes(colour = rgb_spec(Species, sample(Species), sample(Species))))# Or can handle a mix between discrete and continuous p + geom_point(aes(colour = cmy_spec(Petal.Length, Species, Petal.Width)))