Calculates how often a space is covered by a set of ranges.
stat_coverage( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, geom = "area", position = "identity", ..., trim = FALSE, na.rm = FALSE, orientation = NA, show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE )
Arguments
| mapping | Set of aesthetic mappings created by |
|---|---|
| data | The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options: If A A |
| geom | Use to override the default connection between
|
| position | Position adjustment, either as a string, or the result of a call to a position adjustment function. |
| ... | Other arguments passed on to |
| trim | If |
| na.rm | If |
| orientation | The orientation of the layer. The default ( |
| show.legend | logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
|
| inherit.aes | If |
Details
For IRanges and GRanges classes, makes
use of the coverage function. When data is
numeric, be sure to also set the xend or yend aesthetic.
Note
The Ranges classes as x|y are considered closed-interval,
whereas x|y and xend|yend with numeric data are considered open
interval.
Aesthetics
stat_coverage understands the following
aesthetics (required aesthetics are in bold, optional in italic).
x
y
xend (if data is numeric)
yend (if data is numeric)
alpha
colour
fill
group
linetype
size
weight
Computed variables
coverage
coverage scaled to a maximum of 1
coverage integrated to 1
Examples
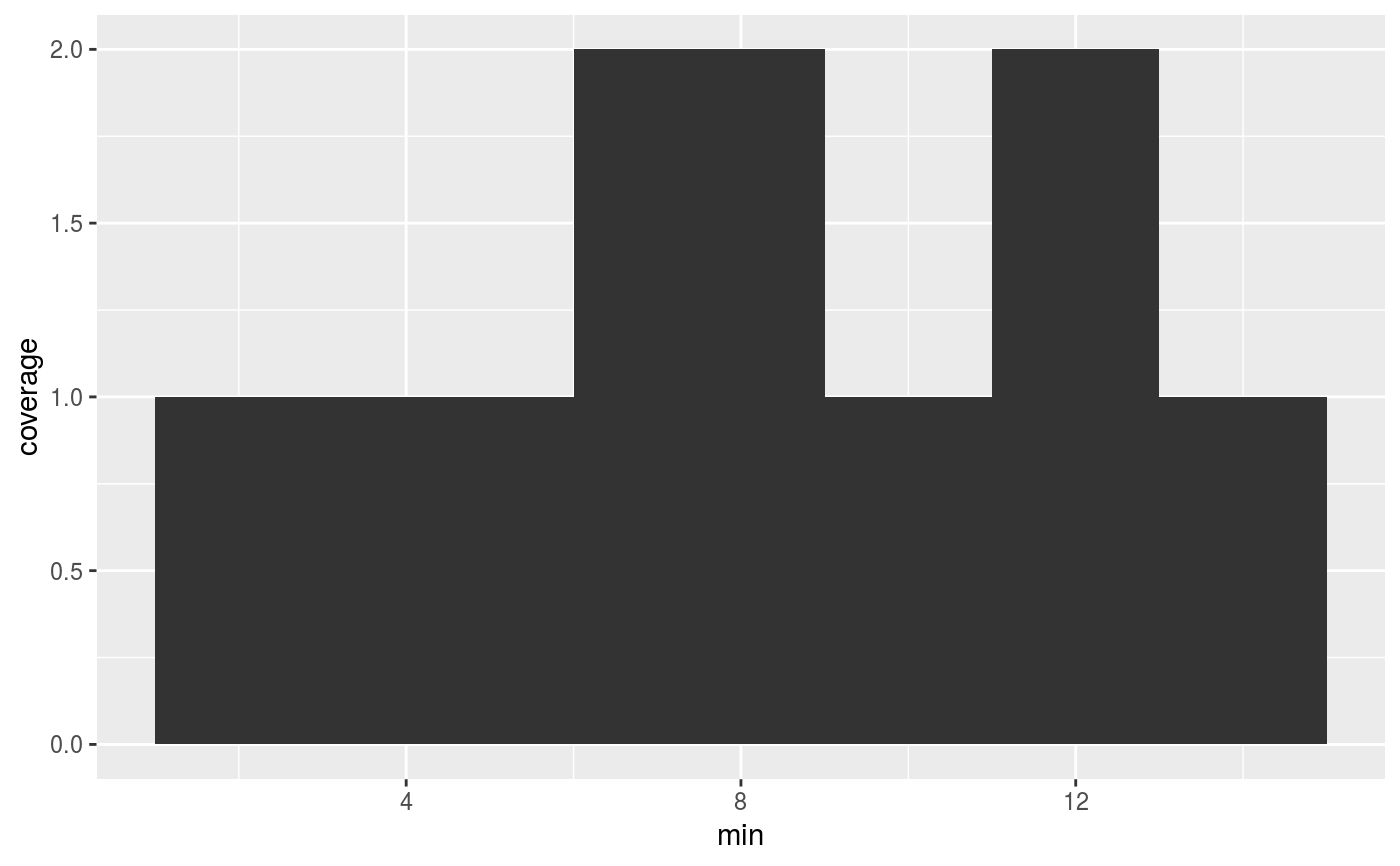
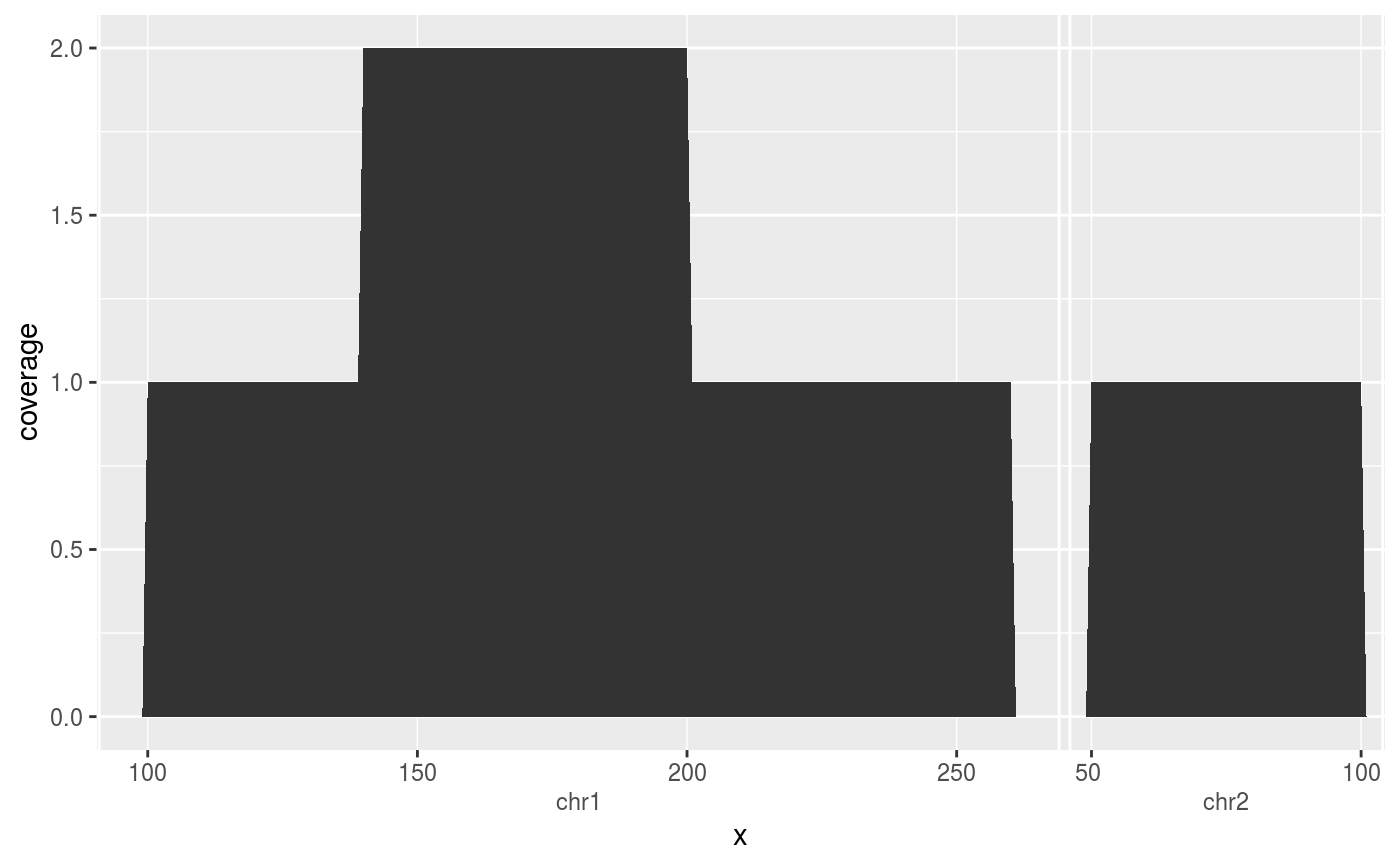
# Computing coverage on numeric data df <- data.frame(min = c(1, 6, 11), max = c(9, 13, 15)) ggplot(df, aes(x = min, xend = max)) + stat_coverage()# Computing coverage on Ranges data require(GenomicRanges) df <- DataFrame(x = GRanges(c("chr1:100-200", "chr1:140-260", "chr2:50-100"))) ggplot(df, aes(x)) + stat_coverage()